Solutions
PRODUCTS AND SOLUTIONS FOR MONITORING AND CONTROL IN THE ENERGETICS
Company ELVAC a.s. is one of the largest Czech companies operating in the field of industrial automation. Our Power Industry Systems division is a manufacturer of monitoring and control systems of the RTU7 series, used mainly in the field of monitoring and control of distribution and renewable sources of electricity, but also in related areas in applications where remote access to information and control of the given technology is needed. Examples of these areas can be, for example, systems for monitoring in water management or air traffic.
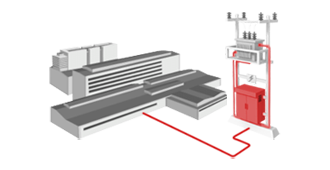
Thanks to the wide scope of our company, we can offer not only stand-alone monitoring and control RTUs, but also, for example, fully equipped control cabinets, HMI interfaces or software such as SCADA, ADMS, software for evaluating data stored in databases, or many other custom-made software systems according to customer needs. In the power industry we are not a manufacturer of power mechanical elements, such as secondary substations, ring main units, load break switches, reclosers, etc., but thanks to many years of cooperation and experience with various manufacturers of these elements, we can design a suitable RTU configuration or complete monitoring and control cabinets for your application, or even recommend suitable power mechanical elements from various suppliers.
Below we describe several typical applications of our RTU systems. The most common applications are further processed in more detail in the so-called application guides (see the tiles above), which also have links from the given application pages, or can be downloaded directly in the Downloads section (see the top menu).